10 Powerful eCommerce Data Collection Strategies & Examples
Leading companies across retail, e-commerce, travel, finance, and real estate need accurate data collection to help them glean actionable insights. Combining manual methods, web research, automation, and AI ensures agility, relevance, and smarter strategies, turning raw data into real business value.
Table of Contents
Moving from face-to-face to online sales is tough for high touch businesses. We’re talking about industries like e-commerce, retail, travel, finance and real estate, where building personal trust is everything. Customers leave clues everywhere, in every transaction and touch point. This data helps retail, e-commerce and travel companies build smarter strategies. For B2B businesses, simple contact and location data can supercharge their marketing. And in financial services, everything from credit scores to insurance claims helps them make better calls on risk.
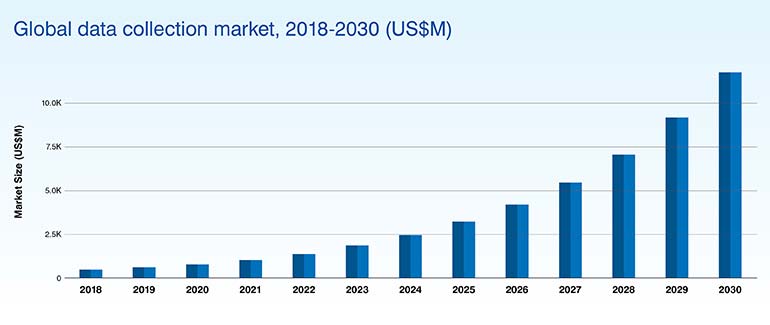
Capturing and analyzing accurate data is so crucial that we need to focus on effective data collection methods. How well you grab, analyze and use these insights really defines your business’s success. The global data collection market is expected to reach USD 11,767.5 million by 2030.
Depending on your business, you can use manual processes or technology like web scraping and data mining. You can also hire data collection company who build your database through web research and other techniques.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through different data collection methods. Our goal is to help you understand the data collection types and techniques out there.
Data collection is the process of gathering structured and unstructured data from disparate sources. It is then measured and analyzed to answer precise questions, validate hypotheses, and support data driven decision-making. Manual data collection methods include surveys, interviews, etc. whereas automated data collection methods include collecting information using web scraping, sensors, and APIs.
Every business runs on data. Leaders use it to make smart decisions, build better strategies, boost efficiency and create better customer experiences. But that data must be accurate. Bad data leads to bad decisions, wasted efforts and revenue loss. Bad data can make you lose your competitive edge.
That’s why your data collection methods must be accurate and tailored to your project. Dirty data really hurts a business. So, you need to invest in effective data collection strategies for your marketing needs. If you don’t have the in-house expertise or the resources to dedicate to data collection, hire the best data collection company. It promises high quality data, reduced operational costs, and reliable analytics to support data-driven decision making.
Here are some stats that prove that investing in good data collection practices is a smart move.
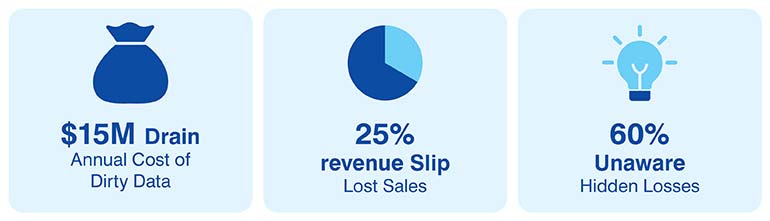
Of course, businesses don’t want to bear such losses, and if it can be saved by following the best data collection methods, I guess every business must take this seriously.
Want to collect accurate data for actionable insights?
Data collection is a technical process and can’t be done randomly. You need to assess your requirement, plan your approach, and select the right methods and techniques. Before you start the process you must understand in detail all about data collection, types, methods and use cases.
For marketing or other business needs, there are basically 2 kinds of data collection methods that are used, primary and secondary. They are collected using different processes and have their pros and cons.
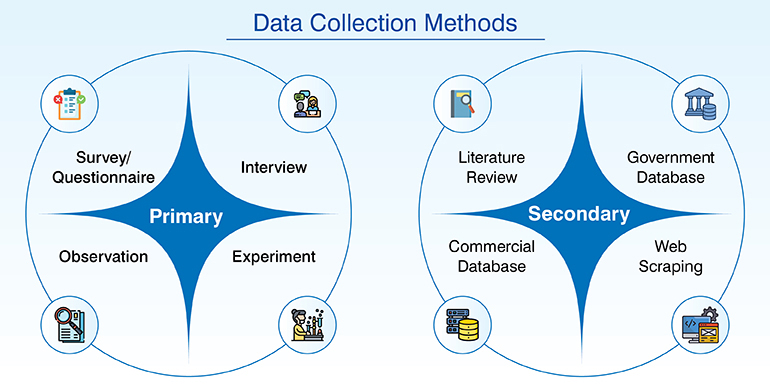
Primary data is the information we collect from a firsthand source. Based on your requirement you customize your approach and collect the exact data relevant to your needs. The data stays original, and you can use the unique data for your sales and marketing. Since you have more control over quality, this data mostly stays accurate, but it is time consuming, expensive and requires manpower.
Surveys, observations, personal interviews, feedback requests, online tracking, social media are some primary data sources. This data can be further understood through a few examples of primary data which would include product reviews directly collected from the website, survey reports, direct property inspections, etc.
When it comes to secondary data you collect what has already been collected by someone before you. Take for instance when you pick data from a website, government publications, blogs, journals, these are all secondary data sources.
Secondary data is easier to collect and often quick but since you didn’t have any control over quality, data accuracy could be an issue. Be a little careful while using this data or run it through some quality check.
Some examples of secondary data would be data from industry research reports, retail trend reports, government records, competitor pricing from an aggregator’s platform, and so on.
Based on your project needs, budget, resources and time you may decide to go for either primary or secondary data collection.
Businesses across industries rely on data collection to support analysis, decision making and automation. The right method depends on the data type, research goal and operational context. Below are ten common data collection methods used in Ecommerce, BFSI, real estate and other sectors to build actionable datasets.
Surveys and questionnaires capture structured responses from targeted populations using pre-defined questions. They produce quantifiable datasets for statistical analysis. Used for measuring customer satisfaction, employee feedback or market preferences at scale. Works well when data standardization is critical.
Example: Ecommerce platforms send post-purchase surveys to customers to measure satisfaction, to identify areas of improvement and enhance product recommendations based on quantifiable insights.
Interviews involve direct questioning of individuals to capture detailed insights. Structured formats follow fixed questions, while unstructured allow open ended exploration. This data is ideal for qualitative research where deeper understanding is required. Useful when context and interpretation are as important as facts.
Example: Real estate firms conduct structured interviews with property buyers to uncover purchase decision factors, to support better property listings and targeted marketing strategies.
Observational research collects data by watching and recording real world behaviors without intervention. Data is non-intrusive and reflects natural actions. Use it when self-reported data is unreliable. It’s effective in physical retail or service environments to study behavioral patterns.
Example:Retailers observe customer navigation in stores to identify high traffic areas, to optimize product placement and improve layout for maximum conversions.
Focus groups bring together selected participants for guided discussion on products, services or concepts. They provide qualitative, perception driven data. Used during product development or campaign design stages to validate assumptions or explore consumer attitudes.
Example: Advertising firms use focus groups to test new campaign messages, to identify emotional triggers and audience reactions before launching large scale promotions.
Web analytics and tracking tools monitor digital interactions such as clicks, navigation and conversions. They produce structured behavioral datasets. These datasets are very useful to understand digital engagement patterns, optimize platforms and track marketing performance. Effective in ecommerce and travel booking systems.
Example: Travel platforms analyse session duration and drop-offs through analytics, to redesign booking flows to minimize abandonment and increase completed reservations.
Experiments test hypotheses by controlling variables. A/B testing compares two or more versions to measure performance differences. Used in digital platforms to validate design, pricing or content strategies and is very effective to optimize user experiences with measurable evidence.
Example: Ecommerce platforms run A/B tests on product page layouts, to see which one converts better and reduces bounce rates, to inform long term platform design.
Looking for accurate data collection to help you make timely decisions?
Reviewing data from already existing documents and records to extract insights is also an effective data collection method. Here information is pre-collected and stored in structured form. Best to be used when historical data or external reports are relevant. It saves a lot of time and resources compared to primary research.
Example: BFSI companies leverage stored credit histories and claim records for predictive modelling, lending risk assessment, and underwriting process automation.
Social media listening extracts conversations, mentions, and trends on social media via specialized tools. It is indicative of live public opinion. It is useful to monitor brand perception, campaign performance, or sector trends. Ideal for marketing and customer support teams.
Example: Consumer brands track sentiment spikes on Twitter following new product releases, allowing for quick response to issues and enhanced customer engagement strategies.
IoT sensors and devices constantly gather machine-generated streams of data. Data is sent in real time for operational monitoring. The data works well for use in logistics, manufacturing, and hospitality industries where measurement and automation are needed continuously.
Example: Sensors are installed by hotels to monitor energy consumption in rooms, detecting inefficiencies and conducting predictive maintenance for cost savings and increased sustainability.
Web scraping and APIs are used to automate the extraction of structured data from sites and systems. They provide high-scale, real-time datasets. It aligns with the requirements for competitive intelligence, price surveillance, and market studies demanding periodic, bulk-level updates in data.
Example: Ecommerce businesses scrape rival websites to refresh product catalogs and dynamically reprice, keeping listings accurate and competitive advantage intact.
Before you pick a data collection method, you must be crystal clear on your goal. Why do you even need this data? Answering that question will help you define the right technique.
Once you decide on the data collection technique you plan to use, you will need to check your budget. Cost implications also cannot be ignored. Say online surveys will always be more cost-effective than in-person interviews.
Look at your timeframe. If your project needs primary data, that’s going to be time consuming. If you’re short on time, secondary data is an option. But for fresh insights, there’s no substitute for primary data.
We usually balance qualitative and quantitative data. For the ‘how’ and ‘why,’ qualitative data works best. But for in depth information backed by stats, you need quantitative methods.
When real-time data is the need, automation, web scraping and APIs are our core tools. RPA works well for repetitive manual tasks. OCR is great for pulling text from unstructured data and data mining can uncover hidden patterns.
Study your requirement and goal well to align it with best-suited data collection method. Or a hybrid approach can also work well, where you combine manual and automation.
Strategic data gathering aligns business requirements with exacting methods to produce actionable intelligence. Every sector calls for customized data collection techniques right from web scraping to surveying to tackle working issues. The result is not information, but data converted into use cases that drive efficiency, compliance, customer engagement, and competitive advantage.
| Industries | Preferred Data Collection Methods | Data Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Ecommerce & Retail | Web scraping, web analytics, customer surveys | Price monitoring, inventory optimization, personalized recommendations |
| Real Estate | Web research, database building, interviews | Property listings enrichment, market trend analysis, buyer preference mapping |
| Advertising & Marketing | Social media listening, focus groups, A/B testing | Campaign performance tracking, audience segmentation, message validation |
| Travel & Hospitality | Behavioral tracking, IoT sensors, web scraping | Demand forecasting, customer experience analysis, dynamic pricing |
| BFSI | Document review, data mining, surveys | Risk modeling, fraud detection, credit scoring |
| IT/ITeS | APIs, web scraping, secondary data review | Competitive intelligence, product benchmarking, technology adoption analysis |
| B2B Businesses | Database building, structured interviews, web research | Lead generation, account profiling, market opportunity assessment |
Leading players in these industries always hire data collection experts who integrate web scraping, data mining, web research, and database building to deliver industry-specific datasets that convert raw information into measurable business outcomes.
But data collection isn’t a onetime task. It’s a living process that changes with your business and the tech around it. Staying agile and open to new tools from automation to AI driven platforms is how you make sure your methods stay effective and future ready.
By looking at a mix of techniques, like surveys, web research or automated integrations, you can fine tune your strategies to really match your goals. The point is not just to gather information. It is to extract data that’s reliable, relevant and actionable.
At the end of the day, how well the data supports our decisions is what we check. If the insights we gather help spot opportunities and solve problems, it becomes meaningful. It shows data collection is actually creating business value from raw data.
What’s next? Message us a brief description of your project.
Our experts will review and get back to you within one business day with free consultation for successful implementation.
Disclaimer:
HitechDigital Solutions LLP and Hitech BPO will never ask for money or commission to offer jobs or projects. In the event you are contacted by any person with job offer in our companies, please reach out to us at info@hitechbpo.com
Leave a Reply